
'length' array attribute will tell us the size of an array (i.e. the number of elements that an array can hold).
Lets implement this on Eclipse IDE:
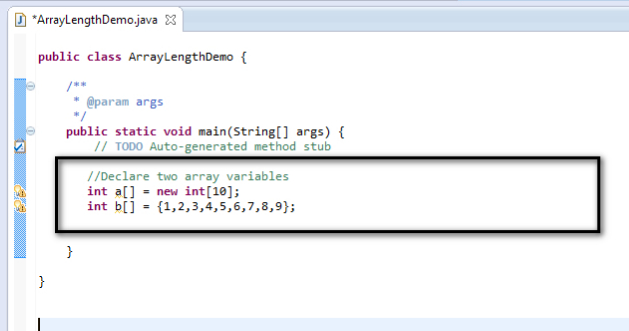
1. Create 'ArrayLengthDemo' class under any project as shown below:
3. Print the size of the declared array variables a[] and b[] as shown below:
4. Save and Run the 'ArrayLengthDemo' class
5. Observe that the output is displayed in console as shown below:
Download this project:
Click here to download the project containing the class file used in this post (You can download the project and import into Eclipse IDE on your machine)
The above example is just for your understanding. Lets create some real time example where you can use this length attribute.
Lets implement the following program on Eclipse IDE
Program: Assign and print the values of array variable with the help of 'length' attribute.
1. Create 'AssingAndPrint' class under any project as shown below:
4. Print the values of all the elements in the array a[] using for loop and length attribute as show below:
5.Save and Run the 'AssignAndPrint' class
Download this project:
Click here to download this project containing 'AssignAndPrint' class file used in this project (You can download this project and import into Eclipse IDE on your machine)
Please comment below to feedback or ask questions.
Please comment below to feedback or ask questions.













5 comments:
Hello arun
here u dint create any class or method with length then how can we take a.length?
@Raghavi - length variable will be automatically created when an array is created. length is a final type variable which holds the size of the array and the value of the length cant be changed.
For example - if we have created the array of size 15 as shown below -
int a[] = new int[15];
Java automatically create a final type variable 'length' with the size of the array assigned to it.
So you can directly use the length variable as explained in the post.
In step 4,
without below mentioned code also we can get the same output:
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
a[i]=i;
}
are there any specific reason for that?
@viki - Without the mentioned code we get the below output -
The value assigned to a[0] is 0
The value assigned to a[1] is 0
The value assigned to a[2] is 0
The value assigned to a[3] is 0
The value assigned to a[4] is 0
The value assigned to a[5] is 0
The value assigned to a[6] is 0
The value assigned to a[7] is 0
The value assigned to a[8] is 0
The value assigned to a[9] is 0
i.e. All the values of the variables printed as 0 as we have not assigned any values to the array elements.
In step4, I have assigned the values to the array elements using the code you have mentioned:
By mentioning this code in the program, I will get the output as:
The value assigned to a[0] is 0
The value assigned to a[1] is 1
The value assigned to a[2] is 2
The value assigned to a[3] is 3
The value assigned to a[4] is 4
The value assigned to a[5] is 5
The value assigned to a[6] is 6
The value assigned to a[7] is 7
The value assigned to a[8] is 8
The value assigned to a[9] is 9
i.e. The value 0 is assigned to first element, value 1 assigned to second elements,....etc are printed in the output.
Hope I clarified your doubt.
the system.out.print statement is not clearly explained. How did we print all the indexes together at one time with this statement.?
Post a Comment